Empower your Child's Reading Journey
The full guide to grade-level reading for SFUSD elementary parents
SFUSD has room for improvement with teaching children to read at grade level. For example, in 2021-22, only 55% of students met or exceeded grade-level standards on end-of-year state tests. Thankfully, SFUSD has recognized that their current approach is failing too many children, and they are in the process of piloting new literacy curricula that will hopefully help improve student outcomes.
In the meantime, SF kids can’t wait. At SF Parent Coalition, we are dedicated to making sure parents and caregivers have the information they need to support their students’ learning now.
This guide is intended to help parents and caregivers assess their students’ reading progress, find ways to support their students’ reading development, and understand whether their students are receiving evidence-based reading instruction in the early grades.

Question 1: Is my child reading at grade level?
SFUSD uses a few different assessments, some of which are new for the 2023-24 school year:
| Grades | Assessment Name | Subject | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| K* | Star Early Literacy** | Early literacy skills, including phonemic awareness and decoding skills | Families will receive score reports that identify each student’s performance level. This assessment is new for the 2023-24 school year, so we’ll share more information about how to make sense of assessment results when more information is available. You can also check the district’s assessment info page here for updates in fall 2023. |
| 1-8 | Star Reading** | Reading comprehension, fluency, and other skills | Families will receive score reports that identify each student’s performance level. This assessment is new for the 2023-24 school year, so we’ll share more information about how to make sense of assessment results when more information is available. You can also check the district’s assessment info page here for updates in fall 2023.
This assessment is replacing the Fountas & Pinnell Benchmark Assessment System (F&P BAS), which is not backed by science. |
| 9-10 (optional in 11-12) | Reading Inventory | Reading comprehension | Students are considered at or above grade level if they score 4 (Advanced) or 3 (Proficient). Students are considered below grade level if they score 2 (Basic) or 1 (Below Basic). Students are also assigned a Lexile score, which helps identify what kinds of books students can read on their own. You can find more information about the Reading Inventory from SFUSD here. |
| 3-8, 11 | Smarter Balanced (SBAC) | Reading comprehension | This assessment is required by the state. Students are considered at or above grade level if they score 4 (Standard Exceeded) or 3 (Standard Met). Students are considered below grade level if they score 2 (Standard Nearly Met) or 1 (Standard Not Met). |
*This assessment is given to students beginning in kindergarten. If needed, some students may be given this assessment in first grade too.
**For students in language pathways programs: In grades K-2, students are assessed in the language of instruction. Beginning in third grade, students are assessed in English; some schools will also choose to assess in the language of instruction.
Glossary of Terms
Phonemic awareness refers to the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words. It is a subcategory of phonological awareness.
Phonological awareness is an important pre-reading skill.
Decoding is the ability to apply knowledge of letter-sound relationships to correctly pronounce written words. Sometimes this is referred to as “sounding out” a word.
Reading comprehension refers to our ability to draw meaning from what we read.
Fluency is the ability to read a text accurately, quickly, and with expression.
Suggested next steps:
- If you haven’t received your child’s test scores this school year, email your child’s teacher and request their latest reading assessment results.
- If your child has different scores on different assessments, ask your teacher for more information about how your child is doing. Some questions you can ask include: Does my child have difficulty reading words? How is my child’s reading fluency? Does my child understand what he’s reading?
- If you only have access to an F&P level (e.g., level A, B, C, etc.), or you feel you have an incomplete picture of your child’s reading abilities, you can try using an at-home reading assessment to get more information. We recommend:
- CBM at Home (Grades K-3 only, in English and Spanish)
- San Diego Quick Assessment (PreK through Grade 11 decoding abilities)
- Learning Heroes’ Readiness Check in English or Spanish (Grades K-8). Note: Learning Heroes also has a Readiness Roadmap (English and Spanish) that provides information about what students should know and be able to do in grades K-8.
- If your child is scoring below grade level on any of these assessments, see section 3 for ways to support your child’s reading growth.
Question 2: How can I help my child if they are reading below grade level?
In some instances, children struggle with reading because of an underlying learning challenge. In other instances, children struggle with reading because they are not receiving effective instruction. Sometimes, children experience both. Ideally, your school can help you determine what is causing your child to fall behind. In the meantime, you can support your child’s reading development with the resources listed below.
Work with Your Child’s School
- Request a “Student Success Team” (SST) meeting from your principal to get more support for your child.
-
- Before the SST meeting: Be prepared to talk about your concerns and observations at the meeting. Bring your own data, including results from the at-home assessments suggested above, a recording of your child reading, and/or writing samples.
-
- During the SST meeting: Ask your child’s teacher about what they’ve observed in your child’s literacy development. Is there anything specific my child struggles with, such as sounding words out or understanding what they’ve read? Ask to see writing samples from class.
-
- During the SST meeting: Ask about what kind of support your child is receiving. Many schools have literacy specialists or ARTIFs (Academic Response to Intervention Facilitators) who meet several times per week with small groups of children who need extra help with reading.
-
- During the SST meeting: If your child is receiving support from a literacy specialist or ARTIF, ask what intervention programs or curricula the literacy specialist/ARTIF uses. Two popular programs, Fountas & Pinnell’s Leveled Literacy Intervention (LLI) and Reading Recovery, are based on discredited theories about how children learn to read. If your child is not yet on track to read at grade-level (see next bullet about asking for data), ask what additional programs might better support your child’s reading development.
-
- During the SST meeting: Inquire about “progress monitoring” and ask to see data. According to the state-adopted Multi Tiered Systems of Support framework, regular progress monitoring assessments should be administered to determine if a student is making gains as a result of intervention provided by a literacy specialist/ARTIF.
- If you suspect your child may have a learning disability, you can request an assessment for special education services.
Work with Your Child at Home
Sometimes kids struggle with sounding out words, sometimes they struggle with comprehension, and sometimes both. If your child is struggling to sound out words, you can try these resources at home:
- Read Not Guess (free!)
- Cox Campus (free!)
- Open Source Phonics (free!)
- Online Decodable Phonics books (free!)
- Reading Rockets (free! And in multiple languages)
- Reading Simplified (e.g., free Switch It game, additional free games)
- How to Teach Your Child to Read in 100 Easy Lessons
Question 3: Is my child getting research-based reading instruction in the early grades?
The early grades, especially kindergarten and first grade, are a critical time in students’ literacy development. This is the time when students should be developing “foundational reading skills” (for example, the ability to identify individual sounds in words and the ability to match letters to the sounds they make) – skills that lay the foundation for students to become proficient readers who can draw meaning from grade-level texts. Decades of research have identified important practices that ensure students develop foundational literacy skills in grades K-1. Unfortunately, discredited practices are still used in some SFUSD classrooms today.
In your child’s K-1 classroom, look for:
| This! 🙂 | Not this! 🙁 |
|---|---|
| These research-based practices will help your child learn to recognize words. | These practices have been discredited by research. |
Decodable books, while students are learning basic spelling patterns, because these books allow students to practice the spelling patterns they’ve been taught during phonics instruction. These books should include spelling patterns that children have already been taught.
  | Leveled or predictable books, while students are learning basic spelling patterns, because these books teach students to guess using pictures, not the letters in words. Using pictures to guess words is an ineffective habit used by older struggling readers. These books often have a level assigned (e.g., A, B, C), and they typically have spelling patterns students have not yet learned. The lower level books often have repeated patterns (see example below).
 |
Encouraging students to use phonics knowledge when they read – which is easiest to do in decodable texts when students are first learning to read. One way to do this is to prompt students to “sound it out” when they come across an unfamiliar word.
 | Encouraging students to use guessing strategies that don’t focus on the letters in the word (for example, using the picture and the first letter of a word, or skipping a word and coming back to guess based on meaning). Some of the reading curricula used in SFUSD encourage guessing strategies, also known as “three cueing.”
 |
| Talking about spelling patterns when teaching students sight words, so that children can connect their phonics knowledge to the spelling of new words – including words that are used frequently in text (a.k.a. sight words). It’s okay to use flash cards to practice sight words – as long as instructors help students identify spelling patterns when a word is first introduced. 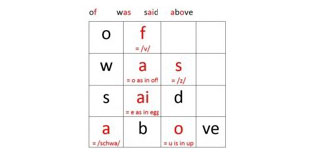 | Memorizing lists of sight words, disconnected from phonics instruction. Research has demonstrated that this approach is ineffective.
 |
Having students apply phonics knowledge when they practice spelling. Spelling and word reading go hand in hand. If your child is given spelling lists or spelling tests, look for words that are similar to the types of words your child is learning to read. 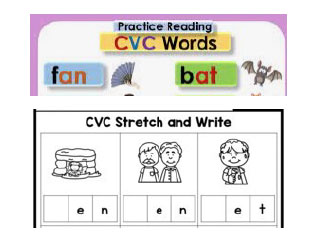 | Regular spelling tests that are disconnected from phonics instruction – for example, if a kindergartener is learning how to read short, three-letter words but their spelling list has words that are much longer. Requiring students to memorize words for tests is unlikely to help them improve their decoding or spelling skills in the long term.
 |
There is much more to reading instruction than teaching foundational skills. If you’d like to learn more about K-1 reading instruction, or you have children in grades 2-12, you can find more information on what to look for in your child’s reading instruction in grades K-12 here. It’s important to note that research offers more information about how to effectively teach some aspects of reading, and less information about how to teach other aspects.
If you want to learn more about why discredited practices are still used in American classrooms today, we recommend the podcast Sold a Story.
But what else can I do to make sure ALL SFUSD kids get the reading support they need?
Get involved in our parent advocacy!
If you want to take action to improve literacy instruction in SFUSD, become a member of the SF Parents network and stay tuned on actions and advocacy to improve reading outcomes for our city's public school kids.

------------
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to SF Parent Coalition board member Jennie Herriot-Hatfield for countless hours spent compiling this invaluable resource for families, as well as these additional contributors who assisted with the development of this resource by helping write it and/or providing feedback: Amy Beck, Kate Franz, Emily Kramer, Julia Lindsey, Lila Nelson, Megan Potente, Douglas Rich, Eva Yabar. We also appreciate SFUSD’s Curriculum and Instruction team for helping us ensure accuracy of the information included.
Download our 1-page Literacy Overview or Send a Copy to a Friend!

